UGM has developed an integrated waste tracking system through the implementation of a waste monitoring system that leverages Information and Communication Technology (ICT). This system enables detailed tracking of waste generated within each department of the Faculty of Engineering, facilitating comprehensive monitoring and assessment of waste production. The ability to monitor waste at the departmental level not only aids in evaluating performance but also informs future improvements.
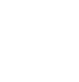
Waste Management in the University Environment (SOP) was issued by the Directorate of Assets UGM, which is derived from the Circular Letter Number 8846/UN1.P.V/Dit-Aset/TR.01.02/2023 signed by the Vice-Rector for Planning, Assets, and Information Systems regarding the waste management in UGM and also the Circular Letter Number 9034/UN1.P/OT.01.03/2024 signed by the Rector.




The amount of waste produced and recycled in UGM is tracked by the Energy and Waste Management Division at Universitas Gadjah Mada’s Agrotechnology Innovation Center (PIAT UGM). A Waste Recycling Laboratory (LDUS) was established in 2011 and renamed in 2016 as part of the Rumah Inovasi Daur Ulang (RInDU). The RInDU also serves as a recycling laboratory that develops various waste and waste recycling methods and technologies.

Upcycling waste into compost, feed, energy, and materials is a sustainable and innovative concept that can have a positive impact on both the environment and society (initiated by PIAT)
Inorganic waste at UGM is treated through three methods: one is through in-house management using specialised equipment available on-site (PIAT UGM), and the other is through collaboration with a third party (RESIKPLUS) and TPA Piyungan.
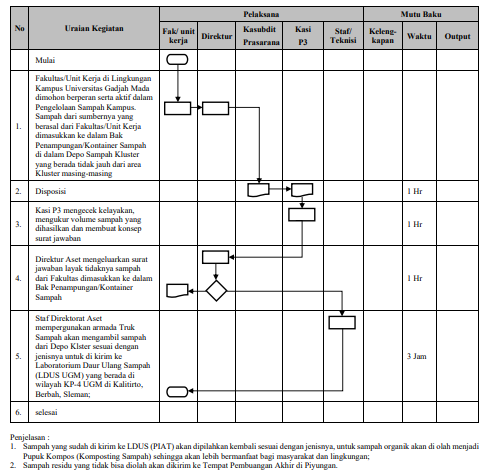
In June 2023, TPA Piyungan was closed because the volume of waste was already full. Since then, Resikplus has treated the total inorganic waste (for instance, there are seven categories of plastic sorted and processed at Resikplus.) For details on this collaboration, you can visit their website via this link: https://resikplus.com/services/.
These initiatives reflect UGM’s commitment to the comprehensive treatment of inorganic waste generated on campus, with approximately 70.87% of the waste being processed. It is more thorough than last year when about 61.83% of the waste was treated.
| Month | Total Anorganic Waste Produces (kg) | Anorganic Waste Treated by Resikplus (kg) | Anorganic Waste Treated by TPA Piyungan (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | 178,490 | - | 76,272 |
| February | 195,740 | - | 76,272 |
| March | 169,070 | - | 76,272 |
| April | 121,110 | - | 76,272 |
| May | 169,480 | - | 76,272 |
| June | 36,660 | - | 76,272 |
| July | 40,425 | 40,425 | - |
| August | 42,459 | 42,459 | - |
| September | 54,000 | 54,000 | - |
| October | 72,000 | 72,000 | - |
| November | 64,451 | 64,451 | - |
| December | 273,335 | 273,335 | - |
| TOTAL | 1,417,220 | 546,670 | 457,632 |
Meanwhile, the amount of organic waste treated is reported here. All the waste in UGM is sorted into three types: organic, inorganic, and residue. Food scraps and other natural waste products are typical organic waste that has been recycled in UGM and reached over 76,82% of the total organic waste.
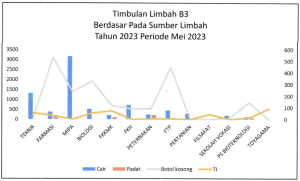
Tracking for toxic and hazardous waste (bahan berbahaya dan beracun (B3)) is conducted by the Occupational and Environmental Security, Safety, and Health Office (K5L). Examples of this type of waste measurement are provided in these two documents 12.3.1 K5L_Pengelolaan LB3 sem 1 th 2023.pdf and 12.3.1 K5L_Pengelolaan LB3 sem 2 th 2023.pdf (see the Figure below). Toxic waste at UGM is 100% treated by two methods: one is through in-house management using specialised equipment available on-site, and the other is through collaboration with a third party (PT. Prasadha Pamunah Limbah Industri and PT. Wastec International). For details on this collaboration, you can visit their website at https://wastecinternational.com/.
The Rumah Sakit Akademik – Perhitungan Limbah B3 dan Penjelasan IPAL
12.3.1 RSA_Perhitungan Limbah B3, Penjelasan IPAL, Limbah Makanan.pdf

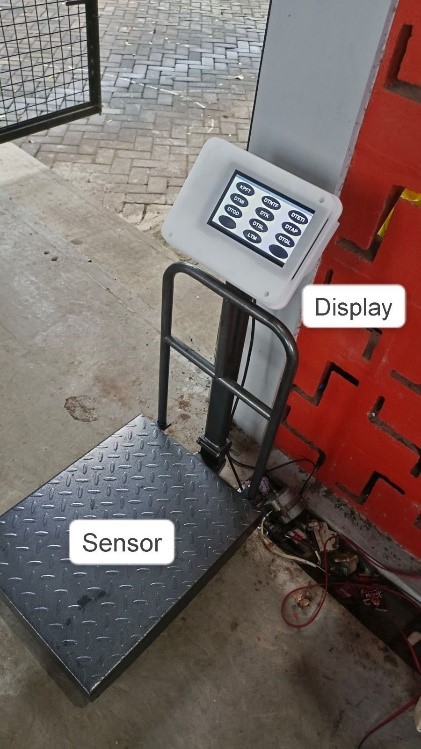
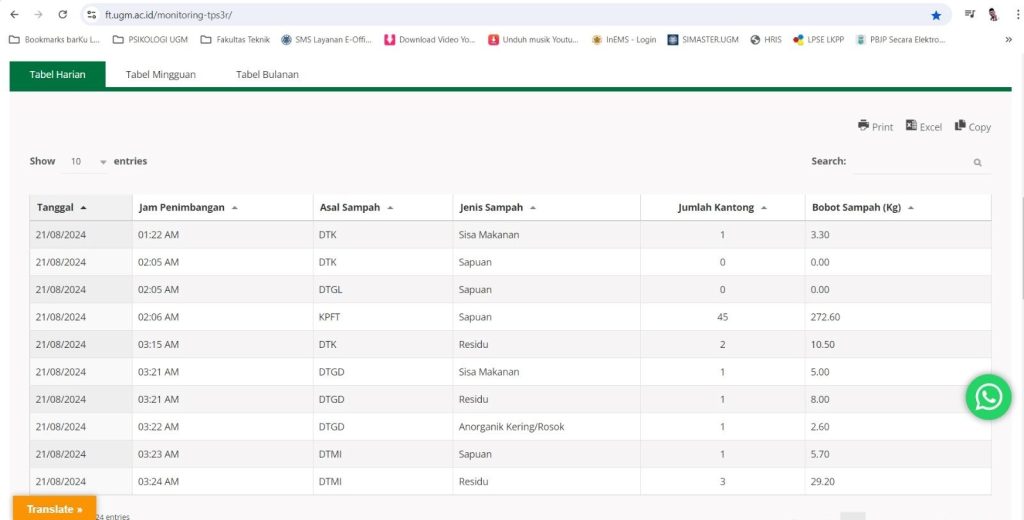
The 3R-based Waste Collection Point named Grahakara Grafika, developed and implemented at The Faculty of Engineering at Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM), demonstrates a waste monitoring system that leverages Information and Communication Technology (ICT). Currently, this waste monitoring system is being developed for implementation across the entire UGM campus and will be integrated with the Campus Management System.
The Faculty of Agriculture also tracks the amount of plastic bottle waste using two units of used plastic bottle collection points. Although the measurement is still done manually, this type of waste collection unit has already helped sort the waste and track the number of plastic bottles used.




The faculty of Animal Science owns a Waste Processing House Facility. The waste processing house is where livestock waste is processed to produce high-value products. The processing activities include processing livestock faeces and leather waste. The waste processing house can be used for research and practicum activities.
FEB implements several strategic programs related to waste management at FEB UGM through processing organic waste into fertiliser that is used to make biopores in the campus environment. In addition, FEB UGM also encourages the reduction of plastic waste by encouraging the use of personal drinking water thermoses (tumblers) for students and faculty members and providing free refillable drinking water through water fountains. This policy is in line with the movement to reduce plastic waste from the consumption of bottled water and beverages in packaging. The recommendation to use tumblers is supported by the availability of water fountain facilities from the UGM Drinking Water Supply System (SPAM).
References:
- Waste Management in the University Environment (SOP)
- Circular Letter Number 8846/UN1.P.V/Dit-Aset/TR.01.02/2023
- Circular Letter Number 9034/UN1.P/OT.01.03/2024
- https://piat.ugm.ac.id/sub-bidang-energi-dan-pengolahan-sampah/
- 12.3.1 K5L_Pengelolaan LB3 sem 1 th 2023.pdf
- 12.3.1 K5L_Pengelolaan LB3 sem 2 th 2023.pdf
- Faculty of Engineering – Waste Disposal Site (TPS) which applies the principle of Reduce, Reuse, Recycle (3R)
- Faculty og Agriculture – – Plastic bottle collection unit can be used to calculate the amount of waste load
- https://ppt.fapet.ugm.ac.id/fasilitas-riset/
- FEB implements several strategic programs related to waste management
- Drinking water thermoses (tumblers) for students
- FEB implements several strategic programs related to waste management