Through its large web of Faculties, Schools, and Research Centers, UGM houses a wide range of research facilities dedicated to advancing environmental sustainability. These centers play a vital role in developing conceptual frameworks, conducting cutting-edge research, and ensuring that knowledge and technology related to environmental sustainability are accessible to both internal academic communities and external stakeholders. The availability of such research not only strengthens UGM’s contribution to solving real-world environmental challenges but also fosters innovation, collaboration, and policy impact at local, national, and international levels. Some of the key research centers at UGM include:
The Center for Environmental Studies
The Center for Environmental Studies (Pusat Studi Lingkungan Hidup, PSLH) organizes and facilitates critical and holistic studies in the field of environment, and disseminates and applies the results of these studies to the academic and general community. PSLH was originally established as a form of concern from the UGM academic community towards various environmental issues in Indonesia. This concern emerged in the 1970s, when massive development in Indonesia was carried out, including agricultural infrastructure, transportation, and mining. Meanwhile, ideas have been put forward about environmental management and environmental impact assessments that need to be carried out to prevent uncontrolled environmental damage as a result of development. At that time, institutions related to the environment began to emerge.
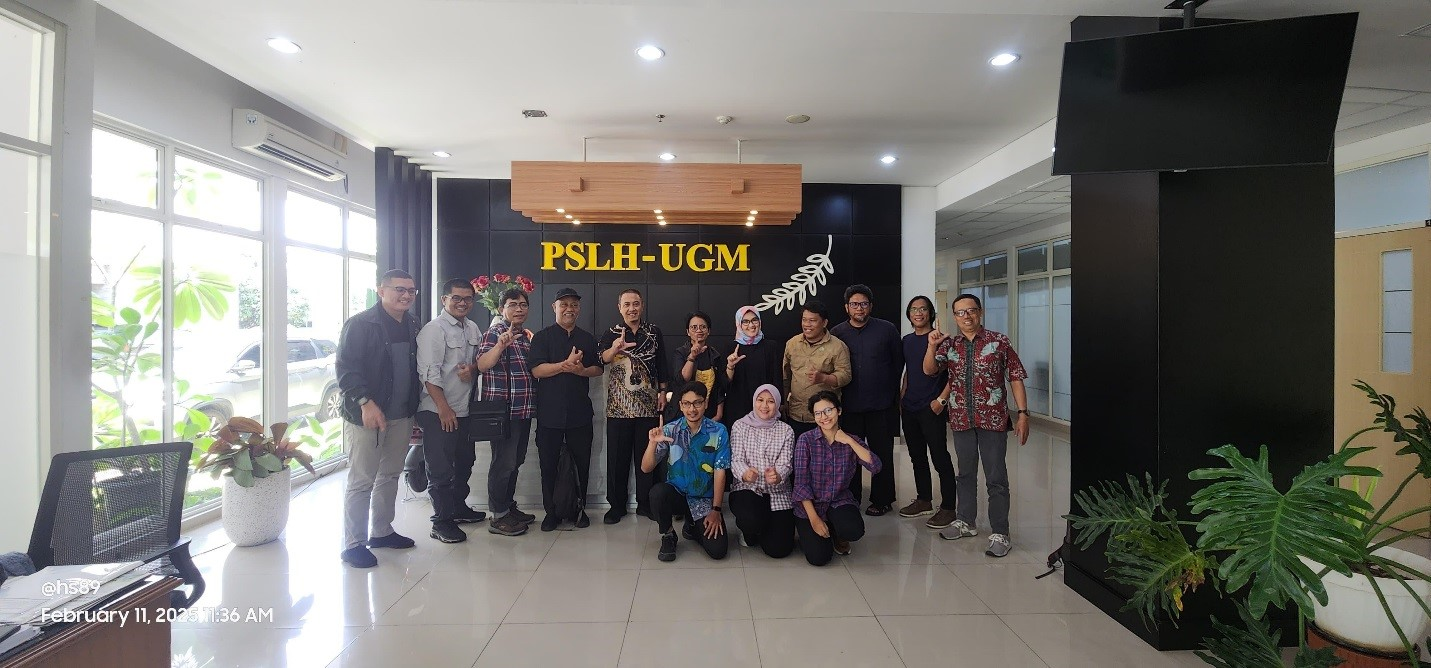

Source: PSLH initiation of collaboration in training, research, and community Service
Through the facilities available at PSLH, UGM is able to contribute to environmental studies and environmental sustainability. For instance, the center is equipped with a storage room for portable laboratory equipment that can be used for research/environmental quality measurement. PSLH UGM also has a number of computers for data processing and a Geographic Information System Laboratory. These facilities are used to the greatest extent by UGM’s Masters and Doctoral students in the field of environment.
The Engineering Research and Innovation Center
The Engineering Research and Innovation Center (ERIC) is an interdepartmental synergy hub under the management of the Faculty of Engineering that facilitates the integration of resources, actors, and interests to produce high-quality research results for the industry, government, and general community. The center was established to become a supporting environment for postgraduate students for their various research-based activities. ERIC has 8 research centers, one of which is a center for environmental sustainability.

Source: ERIC
The Wanagama Eco-Edu Forest
The Wanagama Eco-Edu Forest is one of UGM’s satellite campuses and open green areas. A forest area located in the Gunung Kidul District, it is used as a place of research, field study, and outdoor classroom for students of the Faculty of Forestry, UGM. The forest was initially situated in a karst area, which means the environment was mostly dry and barren. After initiatives to rehabilitate critical land and conserve the forest, Wanagama is now living proof of a sustainable environment that is home to a unique diversity of flora and fauna, including at least 170 plant species, seven bamboo species, 47 bird species, and 17 herpetofauna species. Its vision is to become a globally respected educational university forest known for its support of forest rehabilitation, land rehabilitation, tropical forest management, sustainable eco-tourism, and eco-friendly rural development.

Source: Wanagama Eco-Edu Forest
The Center for Agrotechnology Innovation
The Center of Agrotechnology Innovation (Pusat Inovasi dan Agroteknologi or PIAT) is a center for agricultural innovation based on integrated farming. The establishment of the center was to strengthen agriculture based on environmentally friendly technology innovation and optimization of energy resources. Also known as PIAT, the center is another UGM satellite campus that is used in the learning, research, and community service activities of UGM student and staff. PIAT has two main areas located in Berbah and Mangunan. Besides its research buildings, the areas are dotted with forests, plantations, farms, fields, gardens, ponds, and other supporting facilities; meaning, the center possesses a rich diversity of trees and vegetation. There are several sub-fields of research in PIAT. The Food and Horticulture Sub-field mainly utilises the productive farmland areas, organic gardens, and advanced green facilities like screen houses and vertical farming greenhouses. The Biodiversity Conservation Sub-Field manages genetic seed banks, orchid gardens, and tissue culture labs, Artificial ponds and water retention ponds found on site are used to study water management.
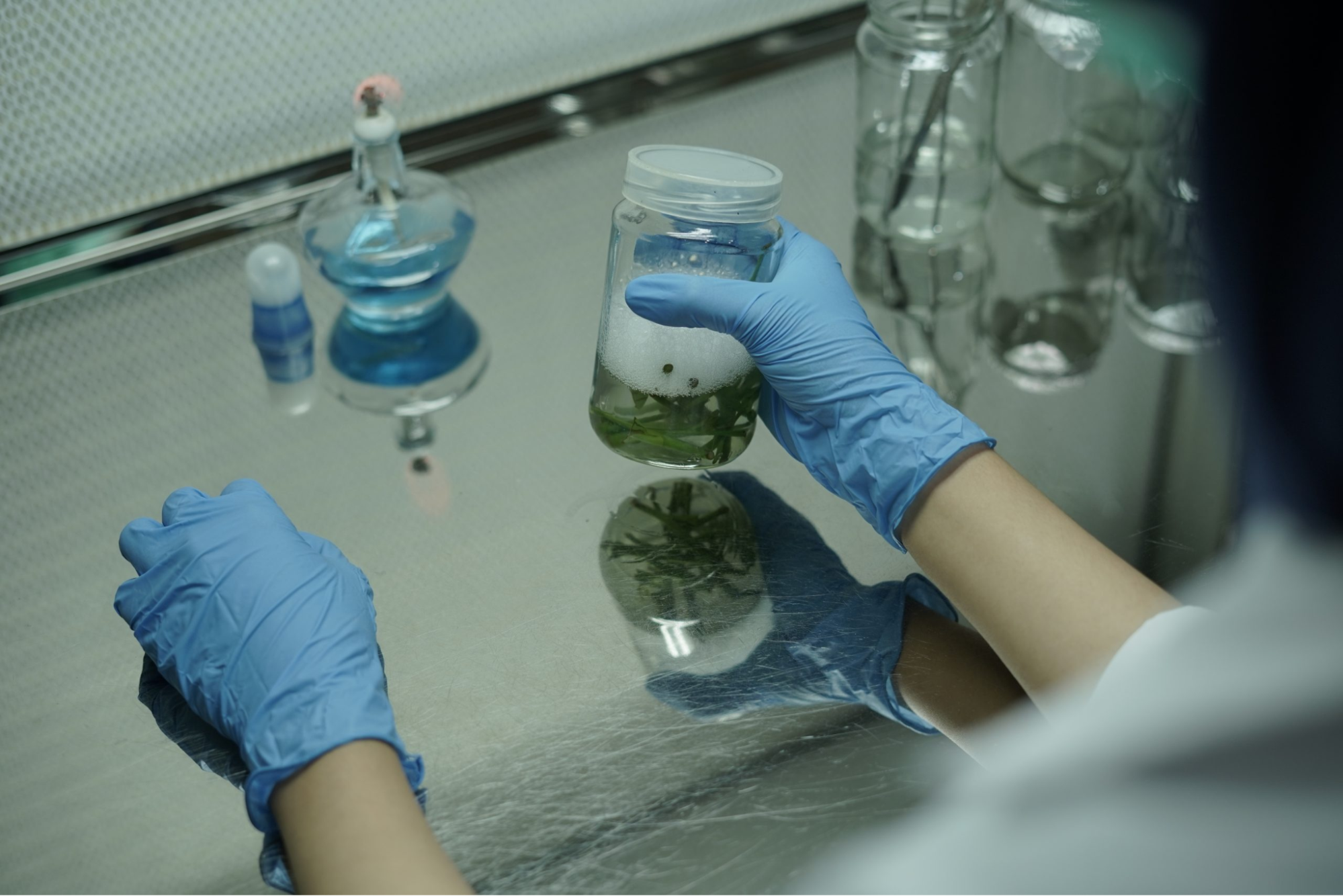

Source: Center of Agrotechnology Innovation
The UGM Science Techno Park
As a socio-entrepreneurial university, UGM’s not only stands as a reference in the development of science, technology, and art. The university plays a role as a catalyst in the human development process, which leads to increased productivity and socio-economic welfare of the Indonesian people. In realizing this mission, the UGM Science Techno Park was mandated to be a productive research and innovation-based vehicle in synergy with Indonesia’s industry and government, and to play a role in the research of environmental sustainability. The research at UGM Science Techno Park focuses on overseeing 5 downstream areas; 1) Health and pharmaceuticals, 2) Agro-industry, 3) New and renewable energy, 4) Manufacturing, engineering and information technology, 5) Heritage, arts, culture and sustainable management. UGM Science Techno Park carries the tagline “Where Innovation Grows” and is expected to be capable of developing the local economy, and increasing the use of local resources to support technological independence in Indonesia.
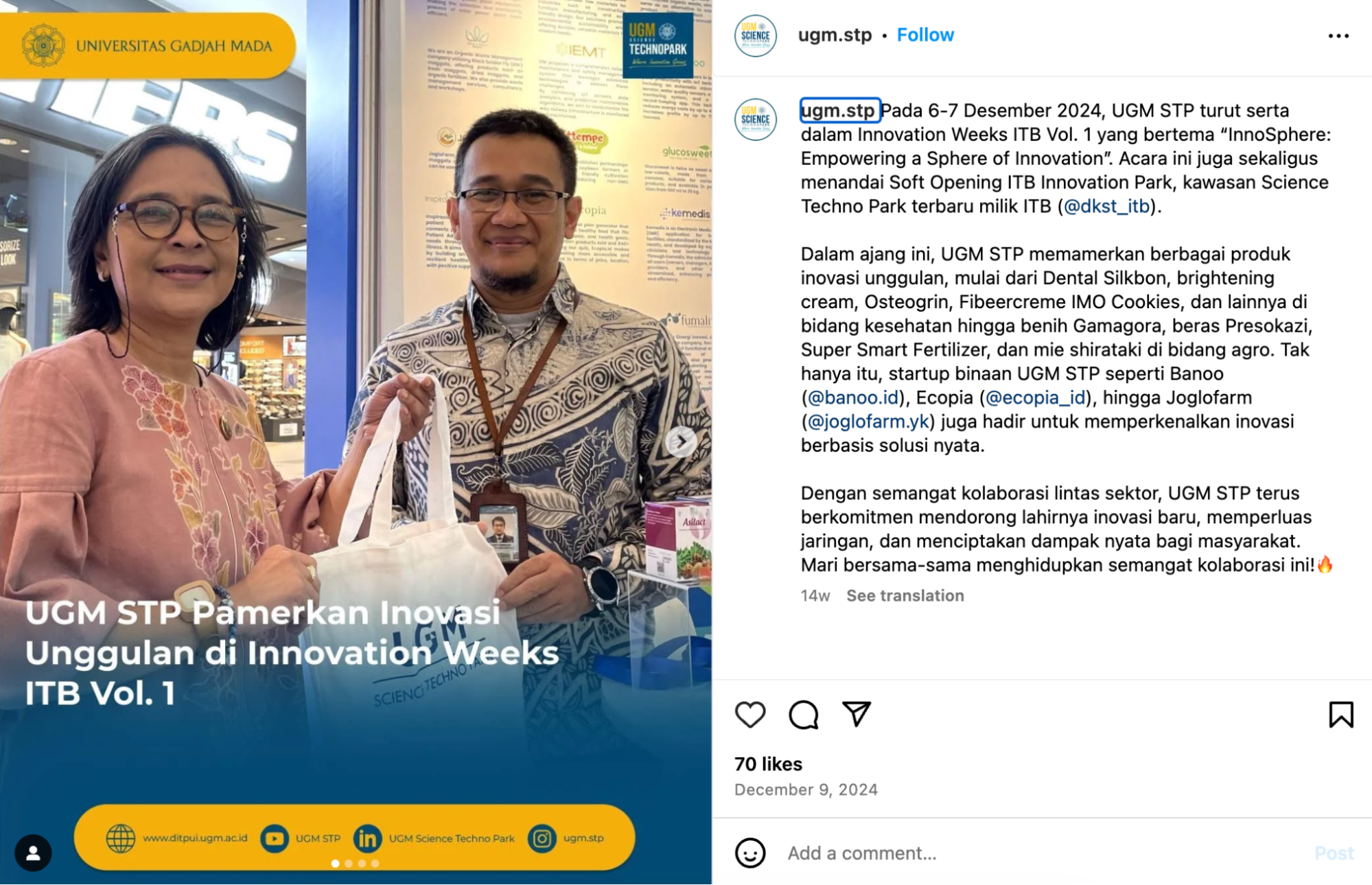
Source: UGM Science Techno Park social media
International Training Center for Cage-Free Innovation and Welfare Hub
Research on sustainable farming practices are closely linked to environmental sustainability because they focus on meeting current agricultural needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs, while also protecting the health of ecosystems. Sustainable farming practices are at the heart of environmental sustainability. These practices protect soil, water, and biodiversity; reduce pollution and greenhouse gas emissions; and promote ecological balance. The research and adoption of these practices will help farmers contribute not only to their own livelihoods but also to the long-term health of the planet.
One concrete example of how sustainable farming practices contribute to environmental sustainability is through the promotion of ethical and eco-friendly livestock systems. By shifting toward farming methods that prioritize animal welfare, environmental protection, and resource efficiency, we help reduce pollution, conserve water and land, and support biodiversity. In this spirit, UGM has its very own International Training Center for Cage Free Farming. This training center is the first of its kind in Southeast Asia. The ITC Cage-Free Innovation and Welfare Hub was built to facilitate layers of poultry farmers, academics, and animal science students to practice cage-free farming. This facility is open to the public, including government agencies and other stakeholders, both for domestic and foreign participants. This training center enables egg producers to achieve success, sustainability, and long-term profitability in battery cage-free egg production. This training center brings together egg producers and other industry stakeholders to improve the long-term sustainability and competitiveness of the egg industry in Indonesia and across Asia.
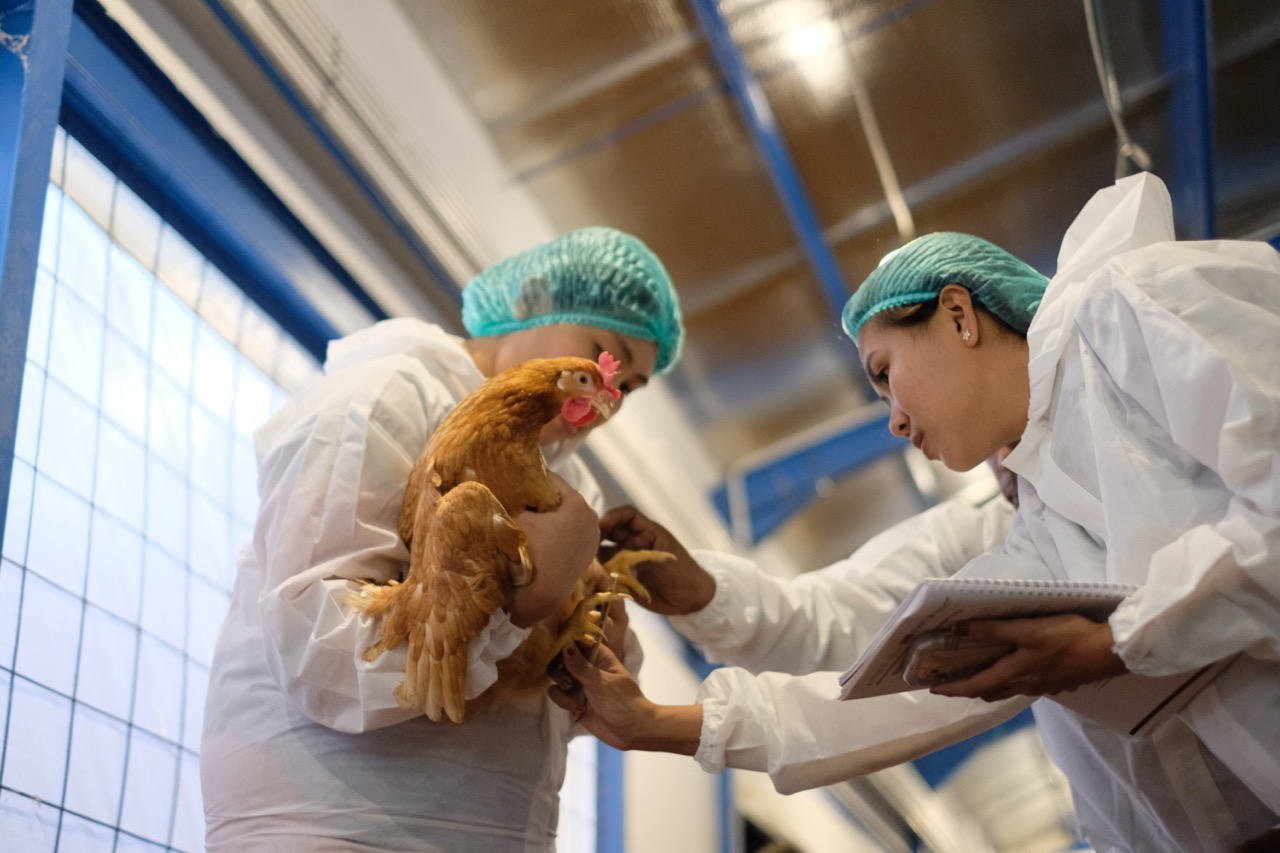

Source: International Training Center for Cage Free Farming
Sustainable farming practices is a key field of study in UGM. Among many groundbreaking research projects, the university has recently succeeded in blending technological creativity with agriculture through Desa Apps, a digital-based agricultural extension and communication application. Desa Apps offers features and serves as a communication/discussion/education space for farmers, extension workers, and experts in the agrocomplex field (agriculture, livestock, and fisheries) to continuously improve the quality of farming and/or breeding businesses in Indonesia; starting from planning, planting, maintenance, harvesting, and farming business analysis. Desa Apps was also developed into a website-based application (Web App) called Lentera Desa, an online education and training platform in the agrocomplex sector, in the hopes that its features and information can reach a wider audience.
Source: Desa Apps
UGM Vocational School Field Research Center
UGM also has its very own Fabrication Laboratory located in the Kulon Progo District which is accessible to the public to support their farming businesses. Under the management of the Vocational School’s Field Research Center (FRC), the Fab Lab is equipped with various technology incubation facilities including cocoa processing, wood pellets, goat’s milk processing, and other technologies to accelerate the quality of local products, especially agriculture and livestock. The establishment of the Fab Lab was made possible through collaboration with the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) in the Technical Cooperation Project which aims to empower the people of Kulon Progo with an open innovation approach. To accelerate the quality of local products, especially agriculture, and livestock, Fab Lab is expected to become an educational and teaching ecosystem that plays a role in creating solutions to problems, as well as educating and downstream its output to industry and society.
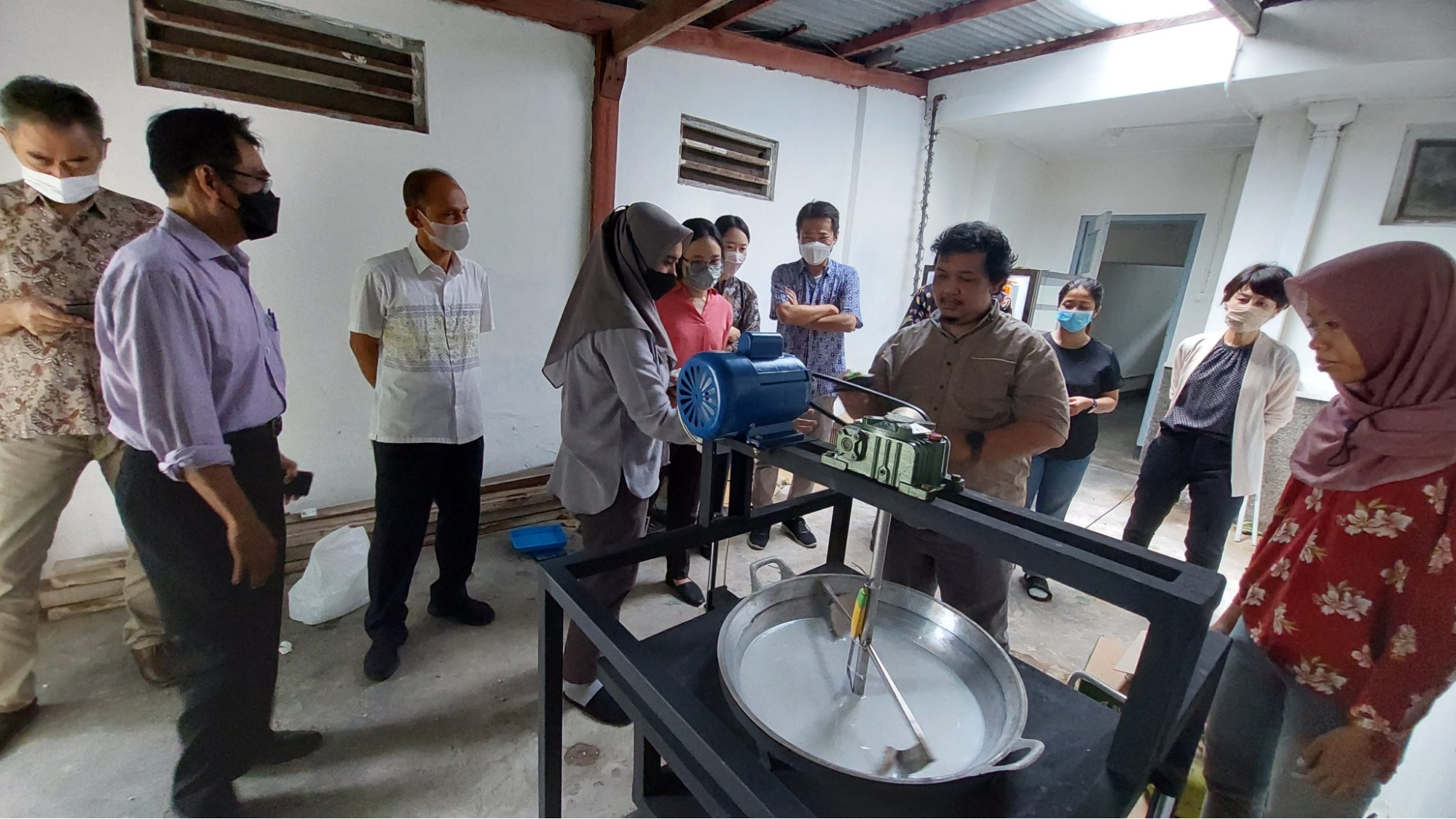

Source: Fab Lab
Sources:
- Center for Environmental Studies
- PSLH initiation of collaboration in training, research, and community Service
- Engineering Research and Innovation Center
- ERIC
- Wanagama Eco-Edu Forest
- Center of Agrotechnology Innovation
- UGM Science Techno Park
- UGM Science Techno Park social media
- Desa Apps
- Digital-based agricultural extension and communication application
- Lentera Desa
- International Training Center for Cage Free Farming
- ITC Cage-Free Innovation and Welfare Hub
- Fab Lab
- collaboration with the Japan International Cooperation Agency