UGM has established comprehensive water quality standards and guidelines to ensure the protection of ecosystems, wildlife, and public health. The university monitors and tests water quality from various sources, including lakes, rivers, and wells on campus, to comply with regional and national regulations. For instance, UGM conducts rigorous water quality testing in line with government standards, such as the Permenkes RI No. 2 of 2023, to monitor parameters like total coliform and E. coli content. The university also employs wastewater treatment systems and water recycling programs to ensure the safe discharge and reuse of water, safeguarding the environment and supporting sustainable campus practices.
Policies on Wastewater Management
A regional regulation on domestic wastewater treatment mandates institutions in the Special Region of Yogyakarta, including Universitas Gadjah Mada, to manage and dispose of their wastewater through proper treatment systems.


Laboratory Waste Management
The university has a procedure for managing laboratory waste so as not to endanger the laboratory and the environment. This procedure includes procedures for implementing temporary storage of laboratory waste in each laboratory room, temporary storage of all laboratory waste, and further handling.

Wastewater Treatment Plant at Academic Hospital
As part of its commitment to environmental sustainability, the Universitas Gadjah Mada Academic Hospital manages waste in accordance with Indonesia’s Ministry of Health Regulation No. 1204/MENKES/SK/X/2004 on Environmental Health Requirements for Hospitals. Solid waste management focuses on source reduction, safe handling of hazardous chemicals, and certified medical waste equipment. Liquid waste is collected in containers tailored to its characteristics and processed through the hospital’s own Wastewater Treatment Plant (IPAL). Effluent quality meets environmental standards set by the Ministry of Environment or local regulations.




Wastewater Treatment Plant at the Faculty of Dentistry
The wastewater management at the Faculty of Dentistry addresses the significant volume of wastewater generated by its large population, including domestic, laboratory, and rainwater runoff.
The Faculty of Dentistry implemented the Wastewater Treatment Plant system to meet safety standards for environmental release or reuse, such as garden irrigation and toilet flushing. The system incorporates eco-friendly technologies like bioreactors, membrane technology, and biofiltration, while residual sludge is repurposed as organic fertilizer, aligning with the green campus concept. Despite challenges like space constraints, diverse waste types, and high operational costs, adaptive systems tailored to campus needs and regular quality monitoring ensure effective management.
The wastewater processed at the Faculty’s Wastewater Treatment Plant is regularly monitored. The institution ensures that the treated water meets environmental standards before being released or reused. Routine evaluations are conducted to assess the quality of the effluent and to identify potential improvements in the treatment system. This ongoing monitoring underscores FKG UGM’s commitment to protecting surrounding ecosystems and maintaining compliance with environmental regulations.

“Mini” Wastewater Treatment Plant at the Bulaksumur Residence
The wastewater treatment at Bulaksumur Residence is conducted using compact, cost-effective “mini” Wastewater Treatment Plants. These smaller systems are designed for limited spaces and employ advanced technologies, including microbubble generators (MBG) to maintain high levels of dissolved oxygen, which enhances the efficiency of bacteria in breaking down organic materials. With components like water tanks, pumps, and pipes, the “mini” IPAL is capable of processing up to 1,555.2 liters of wastewater daily and achieving over 90% chemical oxygen demand (COD) reduction.
Compared to larger installations like IPAL Sewon, the “mini” IPAL offers lower fixed costs and simpler management, making it ideal for household or small-scale applications. Currently under development by the Department of Chemical Engineering at UGM, this innovative system aims to provide an accessible, efficient solution for domestic wastewater management while reducing overall treatment costs for the community.

Implementation of Water Recycling Program at UGM
The picture below shows the Schematic of The Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) or Biological Treatment Process for Greywater (left) and Schematic of the Water Treatment Process for Greywater (left). Several faculties, including the Faculty of Engineering, have implemented a greywater recycling system.
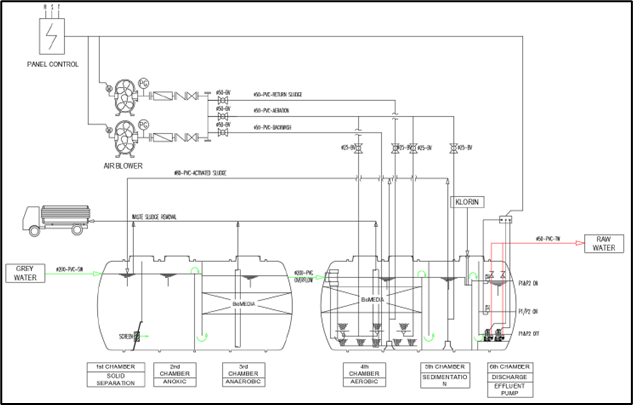
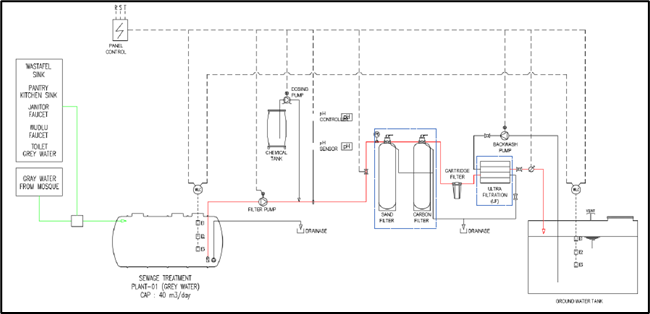
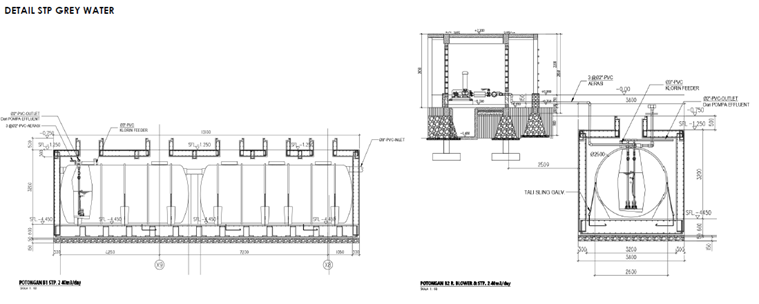
The pictures below depict the ground collector tanks at the UGM residence where the greywater resides after finishing the water treatment process until it is needed. The greywater on campus is recycled to be reused, such as the greywater recycling system on the rooftop of Kinanti Residence (one of UGM’s student dormitories), which is used for flushing toilets and watering gardens. There are also rainwater harvesting and recycling tanks at the Faculty of Engineering and at several UGM Residences, which are part of the campus rainwater harvesting system. Meanwhile, Rainwater Harvesting Systems are injected into UGM’s newly built Learning Centres.







University Mosque Pond


Canal at the Faculty of Animal Science
A water recycling program is the process of collecting, treating, and reusing wastewater for various purposes. Through these programs, we can reduce the need for freshwater and minimise environmental impact. Water from sinks, showers, or stormwater is treated and reused for non-potable applications such as irrigation, toilet flushing, or cooling systems. For further details on UGM’s water recycling program, refer to this page.
UGM has several ongoing water recycling programs.
- Greywater recycling: A system that captures water from dormitory showers and sinks, treating it for reuse in landscape irrigation.
- Rainwater harvesting: A system that collects rainwater from rooftops and reuses it for toilet flushing or garden irrigation. UGM uses both rainwater harvesting systems and ducted rainwater harvesting systems.
- Other water recycling programs include a recycling system for the University Mosque pond, the Faculty of Animal Science, which uses recycled water from the canteen, and UGM, which uses two water recycling methods: upflow and downflow.
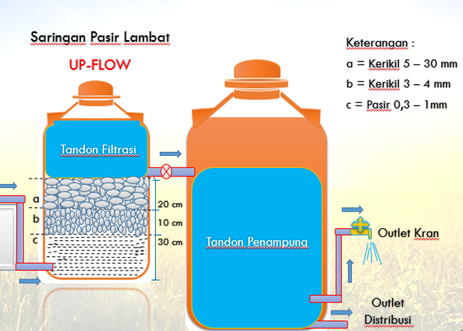
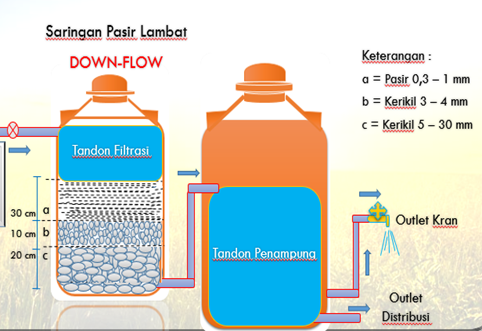
Water Pollution Control on Campus
Each semester, UGM sends teams to conduct quality control of the water available on campus.
- UGM monitors and tests the quality of water sources and bodies of water located inside and near the main campus area, such as the lake in UGM Valley, the shallow wells near faculty buildings, and the Belik and Code River.
- In 2023, UGM widened the parameters of their water quality monitoring study, tracking pollution indicators and water health over the years.
- In monitoring water pollution and quality control, UGM refers to regional and national regulations.
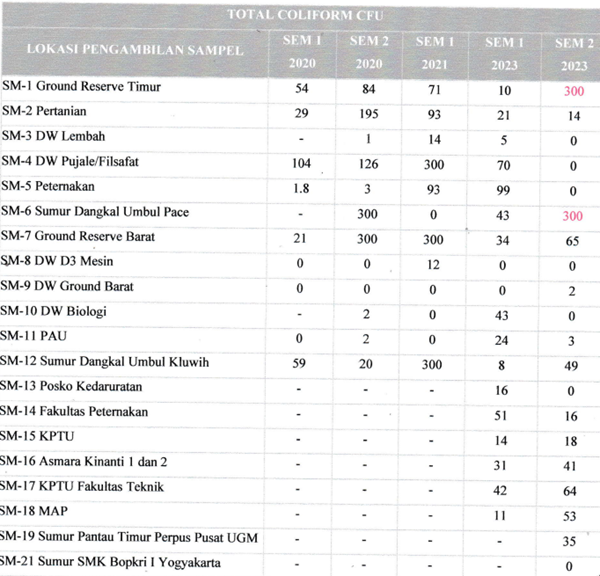
The figures below show the water quality control of UGM Valley Lake and the upstream Code River. In addition, the tabular programme shows water quality monitoring data from several locations over the period 2020-2023. The locations are different water bodies, such as rivers and lakes, in and around the UGM main campus in Yogyakarta, Indonesia. The table is organised by year and semester (SEM 1 and SEM 2), displaying the parameters measured at each site.


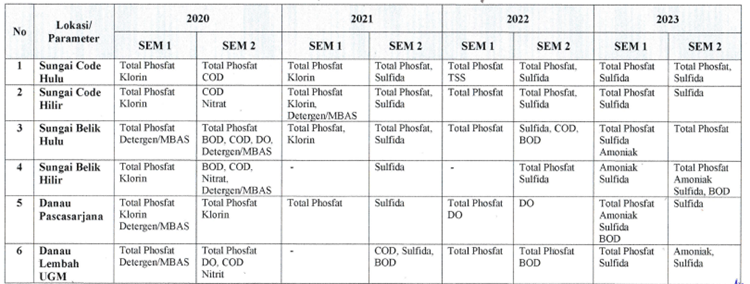
Meanwhile, the table below shows the total coliform count (measured in CFU—colony-forming units) for various water sampling located in UGM over different semesters from 2020 to 2023. Data is used to monitor water quality and safety across these locations, indicating the presence of potential contamination and areas that may need intervention or further investigation.
For further details on water pollution control at UGM, see here.
In conclusion, UGM demonstrates its commitment to environmental sustainability by actively monitoring and testing the water quality of lakes and rivers within and around its campus. These efforts ensure the protection of ecosystems, support biodiversity, and safeguard wildlife, while also promoting human health and welfare. By maintaining high water quality standards, UGM contributes to the preservation of vital natural resources, aligning its practices with broader sustainability goals and fostering a healthier environment for current and future generations.
Further details can be seen in: UGM Preventing water system pollution.
References: